2023 Volvo C40 Recharge Electric operation and charging

Charging in the car’s center display
From the centre display it is possible to set the State Of Charge (SOC), unlock the charging cable, set amperage and schedule charging. To access the charging view in the car’s centre display, tap on and then on Charging. The charging view in the centre display is also activated when charging is started.
Volvo strongly recommends against charging the car with an alternating current of 100-120 V in combination with an amperage below 10 A.
Setting the charge limit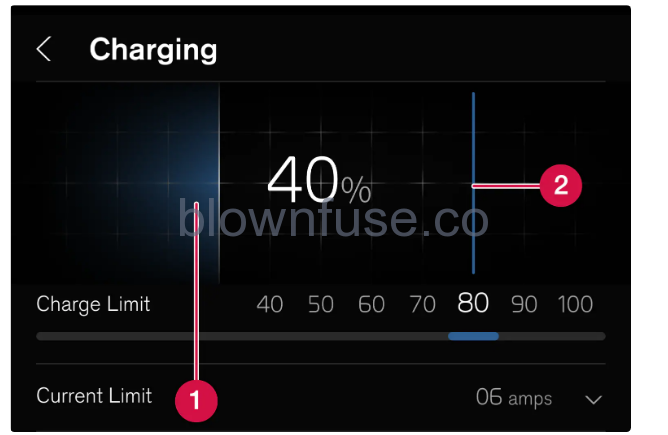
- Battery’s current State Of Charge (SOC).
- Charge limit – Swipe to set a limit for the State Of Charge (SOC) at which the charging should be ended. The set value remains the same until it is changed again in the centre display or via the Volvo Cars app.
Follow the recommendations regarding handling the high voltage battery in order to optimise its service life and performance.
Schedule charging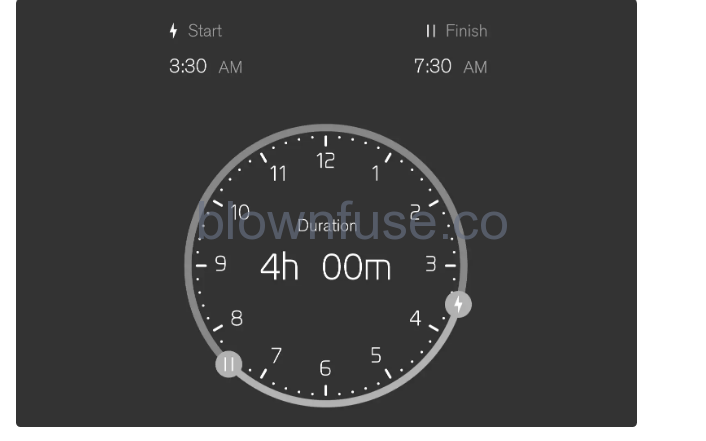
When charging with an alternating current, it is possible to schedule charging and set start and stop times for when charging should take place. Select in the centre display and then activate the scheduling with Schedule charging. Use the controls at and to set the desired start and stop time for charging. Use the control at Schedule charging to deactivate the scheduling of charging.
Temporarily bypassing the settings for scheduled charging
There is the option to temporarily bypass the settings for activated scheduled charging without the need to deactivate scheduling. For example, it may be useful if the car has charging scheduled for during the night but charging is also necessary outside of this time, e.g. when parking after using the car.
- Plug the charging cable into the car – the LED lamp by the car’s charging input socket will illuminate in blue when the car is set to charge according to the set schedule. Charging will not take place if this is done outside the scheduled time.
- Unplug the cable and plug it in again.
The LED lamp by the car’s charging input socket flashes/illuminates in green and the car is charged. The scheduled charging will still be activated next time the car is plugged in for charging.
The charging input socket’s LED lamp indicates status for charging the high voltage battery and not whether the car is consuming power, such as when the climate control is in use. Even if the LED lamp indicates that charging has finished, or that scheduled charging is activated, the car may still draw current from the socket. To avoid affecting the car’s range, current is firstly drawn from the socket and not the battery in order to supply any additional load from the car (such as parking heater, etc.).
Locking and unlocking the charging cable
Tap on Unlock cable in the centre display to unlock the charging cable and end the charging in progress. You can lock the cable into the charging input socket by tapping on Lock cable in the centre display. Charging is then resumed automatically when charging via wall socket/charging station (AC charging). Charging will not be resumed automatically during fast charging (DC charging).
Setting the amperage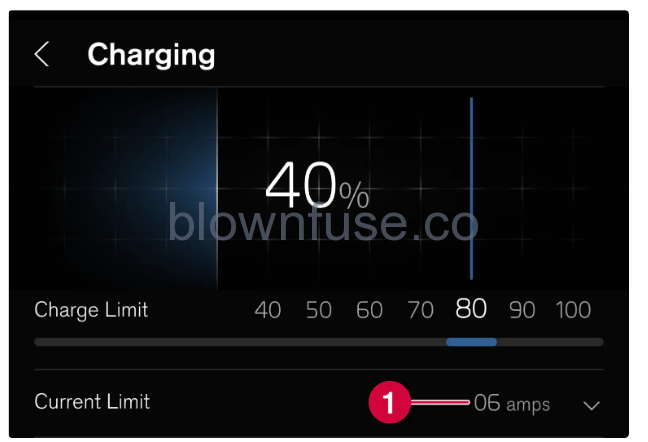
- Set amperage.
When charging with an alternating current there is the option to set the amperage. Select Charging and the arrow at Current (Refers to charging via charging station (mode 3) and charging via wall socket (mode 2).) limit (amps). Tap on + to increase the amperage or – to reduce the amperage.(The set amperage applies per phase from the alternating current source.) When charging with more than 1-phase, an average value for set amperage (Applies to certain markets.) is shown in the driver display.
The amperage may be limited by the charging station, charging cable, or the car’s high voltage system. There is no guarantee that the car can be charged with the specified amperage if it is higher than permitted by the charging station or charging cable.
Drive systems
The car’s electric motor drives the car.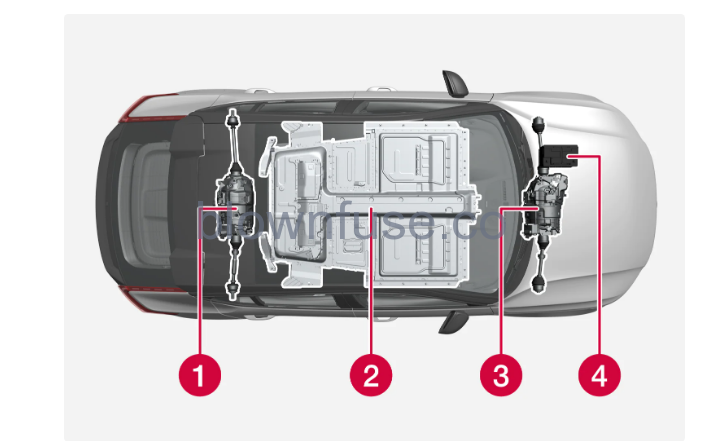
- Electric motor (Applies to cars with two electric motors)– The car contains two electric motors that drive the car and recover brake energy to create electrical energy.
- High voltage battery – The car contains a high voltage battery. The function of the high voltage battery is to store energy. This receives energy by charging from the mains power circuit and by means of
- regenerative braking.
- Electric motor – The car’s electric motor drives the car and recycles brake energy to electrical energy.
- 12 V battery – The car contains a 12 V battery that starts up the car’s electrical systems and powers the electrical equipment in the car.
Symbols and messages relating to electric drive in the driver display
If a fault should occur for the car’s electric drive, a symbol and a message are shown in the driver display. Here are some examples.
| Symbol | Specification |
|---|---|
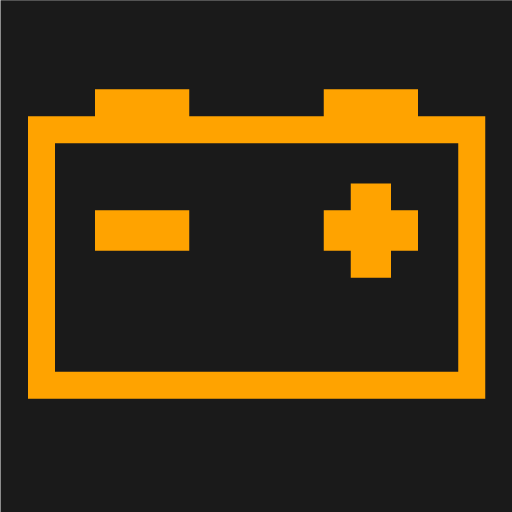 |
Fault in the 12V battery.
Read the message in the driver display. Contact a workshop . |
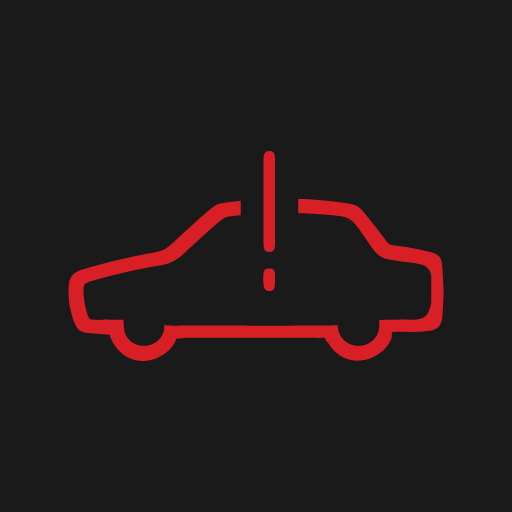 |
Fault in the drive system.
Read the message in the driver display. Contact a workshop . |
 |
Temporary limitation of performance.
Read the message in the driver display. |
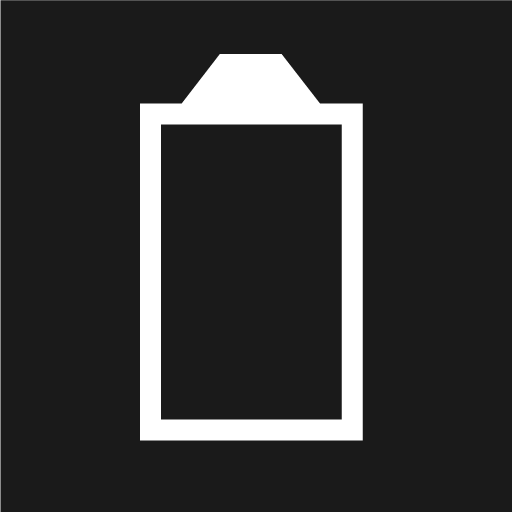 |
Information regarding the high voltage battery’s battery level
Read the message in the driver display. |
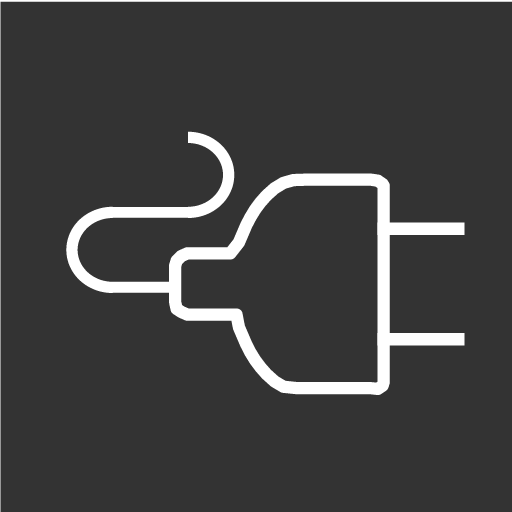 |
Remove the charging cable before starting. |
Recommendations for high voltage battery
Some circumstances may lead to damage to the high voltage battery and shorten its service life. The recommendations are designed for long service life for the high voltage battery and good performance while driving.
Charging
When possible and timely, select AC charging in preference to DC fast charging. AC charging is more sparing on the high voltage battery, especially with regular charging.
High State Of Charge (SOC)
Avoid charging the car to 100% unless the full range is needed for the journey.
The battery may be damaged by maintaining a very high State Of Charge (SOC) for a long time. Therefore, avoid leaving the car connected for charging to more than the recommended charge level, which is shown in the centre display.
Low State Of Charge (SOC)
The high voltage battery may be seriously damaged if it is not charged after being fully discharged. Since there is also a certain amount of consumption and self-discharge when the car is not in use, the State Of Charge (SOC) can fall to 0% if the car is left unconnected with a low State Of Charge (SOC).
If the State Of Charge (SOC) is below 20%, charging is always recommended to avoid the battery being fully discharged.
Long-term parking
To minimise the risk of damage to the battery during long-term parking (longer than one month), it is recommended to have a charging range of 40-60%.
- If the State Of Charge (SOC) is higher – drive the car until the State Of Charge (SOC) is lower.
- If the State Of Charge (SOC) is lower – charge the car.
If you plan to park the car for longer than three months, it is recommended that you connect it to constant charging. Check the car’s State Of Charge (SOC) on a regular basis, as well as that charging is working properly.
Parking in a hot climate
Avoid exposing the car to extreme temperatures. If there is a risk of temperatures around 55 °C (131 °F) then parking for longer than 24 hours should be completely avoided in order to avoid serious damage to the battery. High temperatures can damage the high voltage battery, especially if it is exposed for a long time. If possible, avoid leaving the car unconnected at temperatures higher than 30 °C (86 °F). The car can actively cool the battery while it is parked, but this consumes power and leads to a fall in the State Of Charge (SOC). If the car is charged while it is parked the battery can be cooled without being discharged. If possible, park in the shade if the outdoor temperature is high. Strong sunlight in combination with high outdoor temperature may lead to the car and the high voltage battery becoming very hot.
Parking in a cold climate
At a low temperature for the high voltage battery, performance is temporarily reduced until the battery is heated. Connect the car for charging and use preconditioning to avoid driving with reduced performance. The car can then heat the battery prior to driving without the State Of Charge (SOC) and range falling. Connect the car for charging if parking for longer than 24 hours is planned, while the ambient temperature is below -30°C (-22°F). Driving the car while there is an indication of reduced performance due to low temperature will not be harmful.
Range
The car’s range depends on several factors. The ability to achieve a long-range varies according to the circumstances and conditions under which the car is being driven.
The certified value for the car’s mileage should not be interpreted as an expected range. The certified value should primarily be used to compare different cars and is obtained during special test cycles.
Range in the driver display

When the car is delivered from the factory, or after a factory reset, the range is based on the certified value. When the car has been driven for a while, the range is based on historical driving patterns. The amount of history used depends on the battery’s state of charge. Therefore, the less charge there is in the battery, the faster the range adapts to a changed driving pattern. The estimated range is shown in the driver display when it is less than 50 km (30 miles).
Factors that affect the range
In addition to historical trip data, there are several different factors that affect the range. The longest range is achieved under extremely favourable conditions when all factors have a positive impact.
Examples of factors that affect the range:
- speed
- climate settings
- topography
- preconditioning
- tyres and tyre pressure
- traffic situation
- temperature and weather
- road conditions.
Range in cold temperatures
In cold ambient temperatures, there is a risk that the battery will become too cold, which has a negative effect on the range. This symbol is shown in the driver display if the battery temperature falls to a critically low level. If the car is parked in cold ambient temperatures there is a risk that the range will be reduced dramatically. To avoid substantially reduced range after parking in cold ambient temperatures, the car should be charged while it is parked.
Range-based on speed and outside temperature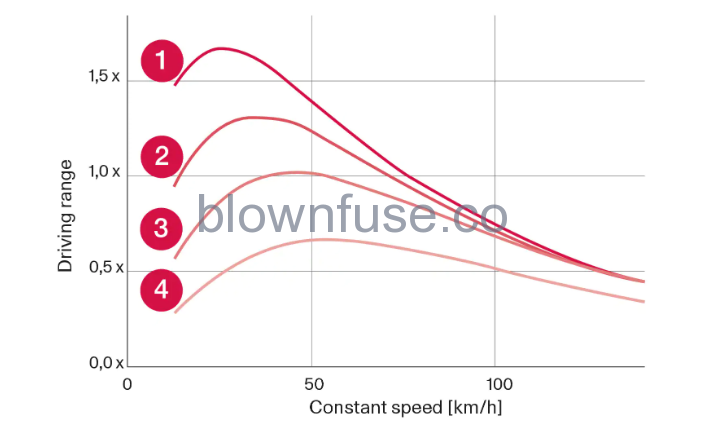
- 20 °C (68 °F) outside temperature and passenger compartment climate Off.
- 20 °C (68 °F) outside temperature and passenger compartment climate On.
- 35 °C (95 °F) outside temperature and passenger compartment climate On.
- -10 °C (14 °F) outside temperature and passenger compartment climate On.
The graph shows the approximate relationship between constant speed and range, where a lower constant speed has a positive effect on range. A higher outside temperature and deactivated climate control are also more beneficial for the range.
Range assistant
The range assistant provides the driver with overview information and assistance in order to facilitate more economical driving. Factors that the driver can influence to extend the range include speed, driving style, and climate settings.
![]()
Speed
![]()
Driving style
![]()
Climate control
Each icon has a gauge that indicates current energy usage. When the gauge changes colour from blue to orange the driver should review his/her energy usage in order to adopt more economical driving behaviour.
Optimising range
The range optimisation function adjusts the climate settings in order to save energy and therefore extend the range of the car.
Activate or deactivate range optimisation via the centre display
- Press .
- Select Range assistant.
- Activating or deactivating range optimisation.
Range optimisation is automatically deactivated at 50% or higher State Of Charge (SOC). In cold ambient temperatures, the output of the heater is reduced. If the climate feels too cold, deactivate range optimisation In hot ambient temperatures, cooling is limited. If the climate feels too hot, deactivate range optimisation Problems with misting may occur since the AC function that adjusts humidity is limited Since the AC function is limited, air recirculation increases, which may lead to a less comfortable feeling of air quality, especially in the rear seat.
Recycling the batteries
Used batteries must be recycled in an environmentally sound manner.
Consult a workshop in the event of uncertainty about how this type of waste should be discarded – an authorised Volvo workshop is recommended. The high voltage battery must only be handled by authorised workshop personnel.

