2023 Volvo C40 Recharge Battery

Replacing the battery in the key
The battery in the key can be replaced when it has discharged. The service life of the battery depends on how much the key is used. The Key Tag (Option/accessory) battery cannot be replaced.

The key’s battery needs to be replaced when the information symbol is illuminated and the The car key battery is low. See Owner’s Manual for replacement. message is shown in the driver display.
Another sign that the battery level is low is decreased range for the key.
The battery in the Key tag (Key Tag) (Option/accessory) cannot be replaced. When the battery is discharged, a new Key tag can be ordered from an authorised Volvo workshop.
Opening the key and changing its battery

Slide the catch by the keyring bracket to the side, and slide the front shell away from the bracket.
>The shell detaches and can be lifted off.
>There is a further catch under the shell to detach the rear.

Slide the catch that was behind the front shell to the side, and slide the rear shell away from the key ring bracket.
>The shell detaches and can be lifted off.
>The battery cover is under the shell.

Turn the battery cover anticlockwise to OPEN position. Use a screwdriver or a coin, for example. Lift off the battery cover. If it is difficult to detach, you can prize it upward using a narrow tool.

The battery (+) side is facing upwards. Loosen the battery by pressing on its edge and then lifting it out.

Install a new battery with the (+) side up. Avoid touching the key’s battery contacts with your fingers. Position the edge of the battery under the two outer plastic catches. Then press down on the battery so that it is held in place by the upper plastic catch.

Refit the battery cover and turn clockwise to CLOSE position.

Refit the rear shell in reverse order to how it was removed. There is no logotype on the rear shell. Press in the shell until you hear a click, and then slide it the last few millimetres to its original position.
>A further click will indicate that the shell is properly positioned and securely attached.
>There must be no gaps remaining.

Turn the key and refit the front shell in the same way as for the rear.
Check that the battery is fitted correctly with the correct polarity. If the key shall not been used for a long time, remove the battery to avoid battery leakage and damage. Batteries with damage or leaks may cause corrosive injury on contact with the skin. Therefore, use protective gloves when handling damaged batteries.
- Keep batteries out of the reach of children.
- Do not leave batteries lying around since they can be swallowed by children or pets.
- Batteries must not: be dismantled, short-circuited or thrown into open flames.
- Do not try to charge non-rechargeable batteries. They may explode.
- Check battery operated products for signs of damage on a regular basis.
The key should not be used if anything indicates that the key or its battery has been damaged or has started to leak. Keep defective products out of the reach of children.
Recommendations for high voltage battery
Some circumstances may lead to damage to the high voltage battery and shorten its service life. The recommendations are designed for long service life for the high voltage battery and good performance while driving.
Charging
When possible and timely, select AC charging (AC is also called alternating current.) in preference to DC fast charging (DC is also called direct current.). AC charging is more sparing on the high voltage battery, especially with regular charging.
High State Of Charge (SOC)
Avoid charging the car to 100% unless the full range is needed for the journey. The battery may be damaged by maintaining a very high State Of Charge (SOC) for a long time. Therefore, avoid leaving the car connected for charging to more than the recommended charge level, which is shown in the centre display.
Low State Of Charge (SOC)
Long-term parking
To minimise the risk of damage to the battery during long-term parking (longer than one month), it is recommended to have a charging range of 40-60%.
- If the State Of Charge (SOC) is higher – drive the car until the State Of Charge (SOC) is lower.
- If the State Of Charge (SOC) is lower – charge the car.
If you plan to park the car for longer than three months, it is recommended that you connect it to constant charging. Check the car’s State Of Charge (SOC) on a regular basis, as well as that charging is working properly.
Parking in a hot climate
Parking in a cold climate
In a low temperature for the high voltage battery, performance is temporarily reduced until the battery is heated. Connect the car for charging and use preconditioning to avoid driving with reduced performance. The car can then heat the battery prior to driving without the State Of Charge (SOC) and range falling. Connect the car for charging if parking for longer than 24 hours is planned, while the ambient temperature is below -30°C (-22°F). Driving the car while there is an indication of reduced performance due to low temperature will not be harmful.
Using jump starting with another battery
If the car does not start, it may be due to the 12V battery being discharged. It can be charged using another car’s 12 V battery or an external charger. Under normal conditions, the 12V battery is charged at the same time as the car is charged, as well as via current transmission from the high voltage battery when the car is not connected for charging. If the 12V battery is discharged for any reason, jump-starting can still be used. This may be caused by the car not being used for a long time, a temporary fault, or a blown fuse in the car’s charging circuit. A discharged 12 V battery needs to be recharged in order to start the car and power its electrical system. After starting, it is possible to start charging the car using the charging cable, which will be necessary if the high voltage battery is also discharged. If the car is out of reach for charging in such a situation, it may need recovery. You need jump leads in order to use jump starting and these are connected to the car’s charging points for the 12 V battery. You will need to remove a number of panels under the bonnet in order to access the charging points.
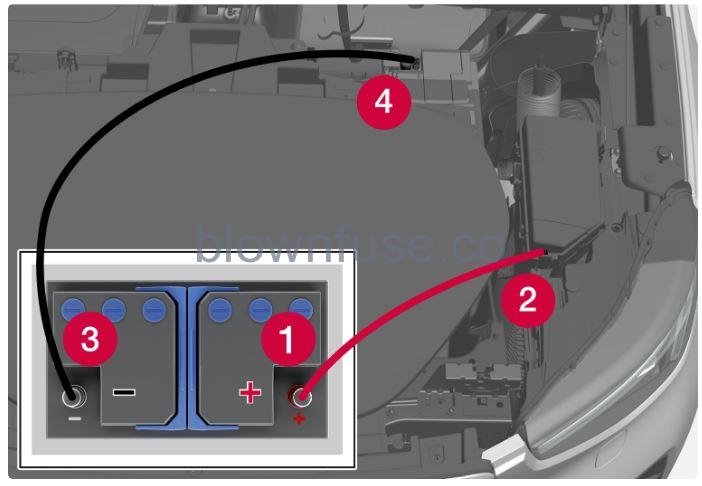 Several of the panels around the storage area need to be loosened for access to the charging points under the bonnet.
Several of the panels around the storage area need to be loosened for access to the charging points under the bonnet.
When jump starting the car, the following steps are recommended to avoid short circuits or other damage:
- Set the car’s electrical system in Passive usage mode.
- Check that the donor battery has a voltage of 12 V.
- If the battery is installed in another car – switch off its engine and make sure that the cars do not touch each other.
- Connect one of the red jump lead’s clamps to the donor battery’s positive terminal (1).
ImportantHandle the jump leads with care. A short circuit may occur if the ends come into contact with surfaces other than the charging points.
- Open the cover (2) for the positive charging point by pressing on its side. This disengages a hook and you can lift the cover up at the same time. There are two connection points under the cover. Use it closest to the centre of the car.
- Attach the red jump lead’s other clamp onto the car’s positive charging point (2).
- Connect one of the black jump lead’s clamps to the donor battery’s negative terminal (3).
- Attach the black jump lead’s other clamp onto the car’s negative charging point (4).
- Check that the jump lead clamps are affixed securely. Poor contact may cause sparks or the clamps to loosen during the starting attempt.
- Start the engine of the donor car.
- Start the car that has the discharged battery by keeping your foot on the brake and selecting gear position D or R.
ImportantDo not touch the connections between cable and car during the starting attempt. There is a risk of sparks forming.NoteFull starting is indicated by means of the driver display’s indicator lamps extinguishing and its preset theme illuminating.
- If the high voltage battery is also discharged, start charging the car with the charging cable.
- Remove the jump leads in reverse order – first the black and then the red. Make sure that the black jump lead’s clamps do not come into contact with the car’s positive charging point, the donor battery’s positive terminal, or the red jump lead’s clamps.
Warning
- The 12 V battery can generate oxyhydrogen gas, which is highly explosive. A spark can be formed if a jump lead is connected incorrectly, and this can be enough for the battery to explode.
- The 12 V battery contains sulphuric acid, which can cause serious burns.
- If sulphuric acid comes into contact with eyes, skin or clothing, flush with large quantities of water. If acid splashes into the eyes – seek medical attention immediately.
- Never smoke near the battery.
Batteries and power supply
The car’s own power supply is connected to several different batteries and components. These make it possible to use the car’s electrical functions. The car’s primary electrical system operates with 12 V voltage and powers electrical equipment. In addition to the primary electrical system, the car has a high voltage system for electrical propulsion.
Batteries
In order to supply power to the various components, your car is equipped with the following:
- a 12 V battery that powers the car’s primary electrical system
- a high voltage battery for electrical propulsion of the car.
Recycling the batteries
Used batteries must be recycled in an environmentally sound manner. Consult a workshop in the event of uncertainty about how this type of waste should be discarded – an authorised Volvo workshop is recommended. The high voltage battery must only be handled by authorised workshop personnel.
Symbols on the batteries
There are information and warning symbols on the batteries.
 |
Use protective goggles. |
 |
Further information in the owner’s manual for the car. |
| Store the battery out of the reach of children. | |
 |
The battery contains corrosive acid. |
 |
Avoid sparks and naked flames. |
 |
Risk of explosion. |
 |
Must be taken for recycling. |
12V battery
The 12 V battery powers the car’s primary electrical system, which includes most of the electrical equipment. However, the high voltage battery is used when the car is run on the electric motor. The battery is dimensioned to power the electrical system and functions that are specific to the car model. Under normal conditions, it is kept charged by the larger high voltage battery.
Handling the battery
- Never disconnect the battery when the car is running.
- Check that the cables to the battery are correctly connected and properly tightened.
- If the battery is held in place by a tensioning strap – make sure that it is always firmly tightened.
Warning
- The battery can generate oxyhydrogen gas, which is highly explosive. A spark can be formed if a jump lead is connected incorrectly, and this can be enough for the battery to explode.
- The battery contains sulphuric acid, which can cause serious burns.
- If sulphuric acid comes into contact with eyes, skin or clothing, flush with large quantities of water. If acid splashes into the eyes – seek medical attention immediately.
- Never smoke near the battery.
Service life and capacity of the 12 V battery
The service life of the battery is influenced by several factors, including number of discharges and climate conditions. If the car is not charged for a long period of time, the battery’s state of charge is reduced due to self-discharge. If the battery is discharged a large number of times, it will negatively affect the service life. A 12 V battery that is kept fully charged has a maximum service life.
Location
12V battery specifications
| Battery type | H6 AGM |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | 12 |
| Cold start capacity (According to EN standard) – CCA (Cold Cranking Amperes) (A) | 760 |
| Size, L×B×H | 277.7×174.4×188.5 mm (10.9×6.9×7.4 inches) |
| Capacity (Ah) | 70 |


